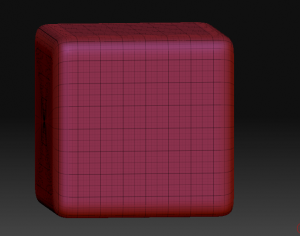
Springs are fun and a handy way to add a common mechanical detail. Zbrush has a built-in spring generator, called the helix primitive. A little setting of the initialize parameters and we get something like this:
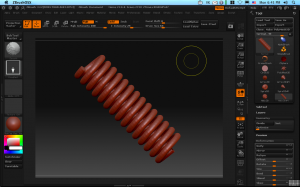
(You did know about the initialize subpallet didn’t you? If not, load up a few 3D primitives in Zbrush and look down the tools menu for the subpallet with “Initialize”. Here you can set all sorts of neat starting shapes for your primitives before making them into a polymesh.)
I didn’t make this a polymesh right away, keeping it as a helix primitive. I’m going to use a little know feature of primitives–col masking. Also, to give me some more resolution, I divided my spring a couple times by going to the geometry subpallet. (Yes, you can divide primitives the same as polymeshes!)
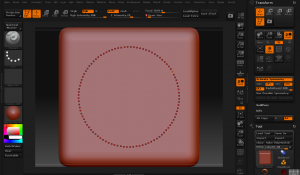
Inside the masking subpallet are some handy features that only work with primitives marked “col”, “row”, and “grid” with a couple mysterious slides marked “sel” and “skip”. You push any of these buttons on an unmasked primitive, nothing seems to happen and thus many a tyro is frustrated by them. This is because these buttons selective remove masks, not add them. (It feels counterintuitive to me too, but this is ZB, after all–which often feels like it was built on “opposite day” at first.)
The sel slider will choose how many adjacent rows or columns of the primitives polygon grid will be selected. The skip slider will then decide how many to skip before selecting. To get a nice box cutout, I’m going to select 3 and skip 4 which will give me a nice alternation. Now, before I go rushing to pushing the “col” button, I do the all important first step–I hit the “mask all” button on the masking subpallet. A press of the magic col button and I have a nice ring mask on my spring:
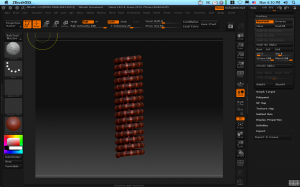
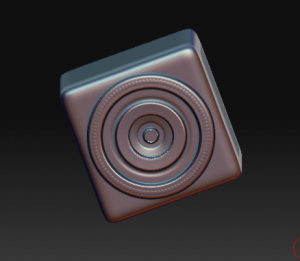
With my plain-jane spring now nicely masked, I can use “inflate” under the deformations subpallet to pull in the unmasked parts to give some additional texture. A little fiddling, and I have something like this:
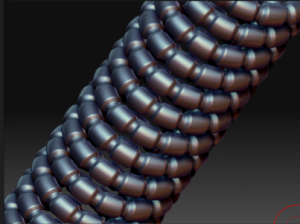
Add a couple of creative cylinders, and I have this: